
Authorized Training Partner
- Understand PMI Philosophy
- Accept code of ethics and professional conduct
- Attend 35-hours of PMP Exam Preparation
- Waterfall PMP and Agile DASM
Are you interested in a PMI Certification?
Are you considering a career in project management or looking to enhance your existing skills? Pursuing a PMI (Project Management Institute) certification can be a transformative step for your professional development. To navigate through the various certifications available and identify the one that best aligns with your career goals, it’s highly recommended to consult with a PMI volunteer or an Authorized Training Partner Instructor. These experts can provide personalized guidance based on your career aspirations and experience level.
Understanding project management principles is invaluable, not only for those directly involved in project management roles but also for professionals across various fields. This foundational knowledge fosters better organization, planning, and execution abilities, which are crucial in today’s dynamic work environments. Even young professionals can significantly benefit from grasping the core concepts of project management early in their careers.
While you consider your options for more formal training or certification, an excellent starting point is the PMI’s KICKOFF™ course. This free, interactive course is designed to teach the basics of project management in just 45 minutes. KICKOFF™ offers a user-friendly introduction to project management, covering essential topics and providing practical tools and templates. Whether you're a student, a budding professional, or even an experienced manager curious about project management, KICKOFF™ provides a valuable and accessible resource to understand the basics and start your journey in the field of project management.
Understanding the PM skills from PMI (Project Management Institute) and having knowledge of the 10 knowledge areas can be immensely beneficial for managing projects across various domains, including research and complex construction. Here are some key benefits:
- Structured Approach: PMI's framework provides a structured approach to project management, ensuring that all aspects of the project are considered and managed systematically. This structure is crucial for both predictable operations and unique, one-time projects like research and construction.
- Improved Planning and Execution: Knowledge of the 10 knowledge areas (integration, scope, schedule, cost, quality, resource, communications, risk, procurement, and stakeholder management) enables managers to effectively plan and execute projects. Each area focuses on crucial aspects of project management, ensuring thorough preparation and implementation.
- Risk Management: Understanding and applying PMI principles helps in identifying, analyzing, and managing potential risks in a project. This proactive approach minimizes surprises and potential setbacks, particularly critical in high-stakes environments like construction and research.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Mastery of stakeholder management ensures that all parties involved in a project are properly engaged and their needs are met. This is vital for securing ongoing support and alignment, which is especially important in projects with many stakeholders, such as public infrastructure projects or collaborative research initiatives.
- Cost Efficiency: Knowledge of cost management enables project managers to develop and control budgets effectively, ensuring that projects are completed within financial constraints. This is crucial in construction projects where financial oversight is essential for profitability.
- Quality Assurance: The PMI framework emphasizes quality management, which helps ensure that project outcomes meet the required standards and deliverables. This is crucial in research and construction, where quality outcomes are directly tied to the success and safety of the project.
- Enhanced Communication: Communication management skills ensure that information is effectively exchanged among all project participants. This leads to better decision-making and more coordinated teams, crucial in interdisciplinary and complex projects like those in research and construction.
Resource Management: Effective resource management ensures that human, financial, and material resources are used efficiently. This is particularly important in construction and research, where resource allocation can directly impact project timelines and outcomes.
- Adaptability and Flexibility: PMI's approach equips managers with the skills to adapt to changes and manage the dynamic nature of projects. This flexibility is essential in research projects, which often explore new frontiers and require adjustments as new information becomes available.
- Professional Development and Recognition: Being proficient in PMI's methodologies not only enhances a manager’s capability but also provides professional recognition globally. This can lead to better career opportunities and credibility in managing complex projects.
Overall, PMI's project management skills and knowledge of the 10 areas provide a comprehensive toolkit for effectively managing diverse and challenging projects, ensuring that they are delivered successfully, on time, on budget, and with the desired quality.
The 10 knowledge areas defined in PMBOK 6th Edition are:
- Project Integration Management
- Project Scope Management
- Project Schedule Management
- Project Cost Management
- Project Quality Management
- Project Resource Management
- Project Communications Management
- Project Risk Management
- Project Procurement Management
- Project Stakeholder Management
In the PMBOK 7th Edition, the focus has shifted from knowledge areas to principles and performance domains. This new edition categorizes project management into three broad domains: People, Process, and Business Environment. Here are the key topics covered under each domain:
People Domain
- Team Leadership: Focuses on skills and activities associated with effectively leading a project team.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involves strategies to effectively engage stakeholders in project decisions and activities.
- Communication: Emphasizes the management and facilitation of communication among all project stakeholders.
Process Domain
- Planning: Encapsulates all aspects of project planning, from scope and schedule to cost and resources.
- Project Work: Involves the management of the actual project tasks and activities to meet the project objectives.
- Delivery: Focuses on meeting project requirements and achieving customer satisfaction.
- Measurement: Deals with the tracking of project progress and performance against defined metrics.
- Uncertainty: Encompasses risk management and the ability to handle ambiguity and changes during the project lifecycle.
Business Domain
- Compliance: Covers the understanding and adherence to applicable laws, regulations, and organizational policies.
- Benefits Realization: Focuses on ensuring that the project delivers the intended business value and benefits.
- Value Delivery: Involves optimizing the flow of value through various project management practices.
The shift from knowledge areas to performance domains in PMBOK 7 aims to provide a more holistic view of project management, emphasizing the versatility and adaptability required for effective project leadership in various business environments.
Blog
PMI-CP as a Strategic Tool for Mega Projects

The PMI Construction Professional (PMI-CP) certification is emerging as a pivotal credential for navigating the complexities of today’s mega construction projects. While traditional project management certifications offer a foundation in planning and coordination, PMI-CP fills a critical gap—translating best practices into field-executable systems that integrate scope, change, quality, and risk into one continuous performance assurance model.
This article is based on Dr. Emari’s presentation on Thursday, May 22, for the PMI Chicagoland Construction PM SIG event!
What is CPMP?
Construction Project Management Professional (CPMP) is a designation that represents expertise in managing and leading construction projects from inception to completion. This role is crucial in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industries, where projects are often complex and involve multiple stakeholders. A CPMP is not just a project manager but a specialized professional equipped with a deep understanding of construction-specific challenges, methodologies, and technologies.
Key Competencies of a CPMP
A CPMP possesses a broad set of competencies that span technical, managerial, and interpersonal skills:
- Civil & Environmental Engineering: CPMPs have a robust understanding of construction principles and practices, ensuring that projects comply with environmental regulations and sustainability practices.
- Construction Engineering & Management: This involves detailed oversight throughout the project’s lifecycle, ensuring that all phases of construction are executed as planned, within budget, and on schedule.
- Safety and Quality Supervisions: A CPMP ensures that all construction activities meet the highest safety and quality standards, safeguarding the health and well-being of workers and the public.
- Business and Strategic Management: They align construction projects with broader business objectives, employing strategic planning to maximize return on investment and ensure project viability.
- Interpersonal Skills for Team Building: Effective communication and team leadership are critical, as construction projects typically involve diverse teams with various technical expertise.
- Innovations & Technologies: CPMPs are at the forefront of incorporating new technologies such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and sustainable construction practices into their projects.
- Integrated Project Delivery (IPD): They often use IPD, a collaborative project delivery method that integrates people, systems, and business structures to optimize project results, increase value to the owner, reduce waste, and maximize efficiency through all phases of design, fabrication, and construction.
Essential Methodologies and Technologies
CPMPs utilize a variety of methodologies and certifications to enhance their proficiency and adaptability in the field:
- PMBoK: Project Management Body of Knowledge offers a standardized framework tailored specifically to the construction industry in PMI’s Construction Extension.
- USACE CQM and AGC CM-BIM: These certifications ensure quality management and proficient use of BIM in project management, crucial for modern construction projects.
- USGBC LEED: Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design certification, which is paramount for CPMPs focusing on sustainable building practices.
LEAN Construction: This approach focuses on minimizing waste and maximizing value, using techniques adapted from the manufacturing industry.
The Role of CPMPs in Today’s Construction Industry
Today’s construction projects are more than just building structures; they are about creating sustainable, efficient, and economically viable spaces. CPMPs play a critical role in steering these projects towards success, making strategic decisions that align with long-term environmental and economic goals. They are pivotal in implementing change management projects, especially in research and development within the AEC industry, which continually adapts to new challenges and technologies.
Who is a CPMP?
- Civil & Environmental Engineering
- Construction Engineering & Management
- Safety and Quality Supervisions
- Business and Strategic Management
- Interpersonal Skills for Team Building
- Sustainability, Innovations & Technologies
- IPD Integrated Project Delivery
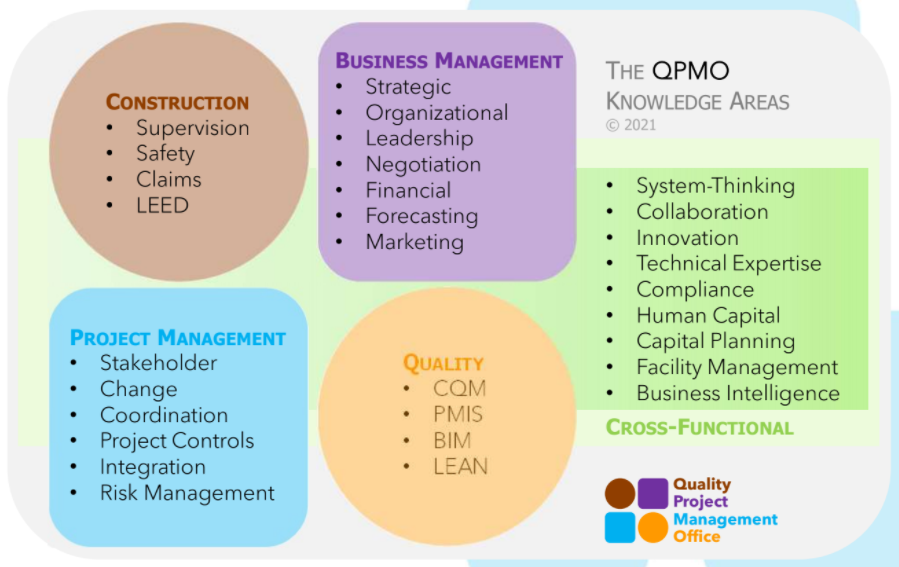

Methodologies & Technologies Used
- PMBoK
- USACE CQM
- USGBC LEED
- AGC CM-BIM
- LEAN Construction
- CQM & CII
- LEED, System Thinking & IPD
Developing a Successful Program

Are you ready for the Future?
Implement Change Management Projects for Research & Development in AEC Industry
Take Action
The role of a Construction Project Management Professional is both challenging and rewarding. As the construction industry continues to evolve with new technologies and methodologies, the demand for skilled CPMPs will only grow. These professionals not only ensure the successful completion of construction projects but also lead the way in innovation, sustainability, and efficiency in the built environment. If you are looking to make a significant impact in the construction industry, pursuing a career as a CPMP could be your path to shaping the future of construction.
Blog
Apply PMBoK to Construction Projects

You are asked to apply PMBoK as Construction Project Management Professional on a new project, where do you start?
PMBoK starts the 10 knowledge areas with a chapter called Integration Management. There are experts in every other knowledge area that could assist the Project Manager except the coordination, communication, and integration of all project management efforts performed by the PMP as discussed in the Integration Management chapter!
Per PMI’s Construction Extension, the main interpersonal skills of a CPMP in a project are Leading, communicating, negotiating and problem solving issues as they arise during the completion of the Project Management processes.
Construction Management in High-Reliability Organizations
As a construction management professional working in high-reliability organizations (HROs), particularly in Facility Management and Operations, I’ve gained invaluable insights into ensuring contractor assurance and managing contracts effectively. In these environments, where safety, quality, and reliability are paramount, it’s critical to have a robust and versatile Construction Project Management Program (CPMP) that addresses the diverse challenges of the construction industry.
This reflection led me to develop a comprehensive 10-Knowledge Area Construction Project Management Methodology tailored for the dynamic needs of our industry. Below, I’ll share an overview of these knowledge areas, the documents produced in each, the metrics tracked, and why they are essential.
The 10 Knowledge Areas of CPMP
1. Strategic Leadership and Scope Integration
Why It Matters: Ensures the project aligns with organizational goals, defines clear scope boundaries, and integrates leadership into project planning.
Key Documents: Project charter, work breakdown structure (WBS), scope statement, change management logs.
Metrics Tracked: Scope completion rate, change request count, alignment with organizational goals, and cost/time variances due to scope changes.
2. Stakeholder Alignment and Organizational Coordination
Why It Matters: Facilitates seamless communication, ensures stakeholder engagement, and resolves conflicts early.
Key Documents: Stakeholder register, communication plan, decision logs.
Metrics Tracked: Stakeholder satisfaction score, issue resolution time, participation rate in meetings, and milestone approval rates.
3. Risk Mitigation and Regulatory Compliance
Why It Matters: Identifies and mitigates risks proactively while ensuring compliance with legal and safety regulations.
Key Documents: Risk register, compliance audit reports, contingency plans.
Metrics Tracked: Number of risks mitigated, regulatory compliance rate, incident reports, and contingency budget utilization.
4. Systems Engineering and Integrated Safety Management
Why It Matters: Incorporates technical systems management with safety protocols, ensuring seamless and secure project execution.
Key Documents: Safety plans, engineering system specifications, equipment logs.
Metrics Tracked: Safety incident rate, system failure occurrences, training completion rate, and compliance with safety protocols.
5. Schedule Optimization and Lean Workflow Planning
Why It Matters: Keeps the project on track by optimizing schedules and implementing lean practices to reduce waste and delays.
Key Documents: Master schedule, lookahead plans, critical path analysis.
Metrics Tracked: Schedule performance index (SPI), milestone completion rates, rework rates due to scheduling issues, and lead time reduction.
6. Financial Oversight and Earned Value Performance
Why It Matters: Ensures financial health by tracking project costs, budgets, and earned value metrics to maintain profitability.
Key Documents: Budget reports, cost variance analysis, earned value management (EVM) reports.
Metrics Tracked: Cost performance index (CPI), earned value vs. planned value, cost variance, and profit margins.
7. Supply Chain Coordination and Procurement Excellence
Why It Matters: Streamlines procurement processes and ensures vendor performance aligns with project requirements.
Key Documents: Procurement plans, vendor contracts, material delivery logs.
Metrics Tracked: On-time delivery rate, procurement cost variance, vendor performance scores, and inventory turnover rates.
8. Legal Oversight and Project Delivery Governance
Why It Matters: Mitigates legal risks and ensures smooth project delivery by adhering to contractual obligations.
Key Documents: Contracts, claims logs, turnover documentation.
Metrics Tracked: Claims resolution time, litigation costs, contract compliance rate, and delivery acceptance rate.
9. Quality Management and Deliverable Assurance
Why It Matters: Guarantees that all deliverables meet or exceed the required quality standards.
Key Documents: Quality checklists, nonconformance reports (NCRs), inspection logs.
Metrics Tracked: Inspection pass rate, rework costs, defect resolution time, and owner satisfaction scores.
10. Environmental Stewardship and Social Sustainability Integration
Why It Matters: Incorporates environmental and social considerations into project planning and execution for long-term sustainability.
Key Documents: Environmental impact assessments, sustainability plans, community engagement reports.
Metrics Tracked: CO2 emissions, percentage of materials recycled, sustainability certification progress, and community satisfaction scores.
Why This Matters to the Construction Industry
This methodology ensures a systematic, integrated approach to construction management, making it applicable across a wide range of projects, from facility management to large-scale infrastructure initiatives. By addressing every facet of project management, from strategic leadership to environmental impact, this framework is designed to:
- Improve decision-making with actionable data.
- Prevent safety incidents and ensure legal compliance.
- Streamline operations for greater efficiency and profitability.
- Deliver projects that meet quality standards while being environmentally responsible.
Connect on LinkedIn
Call to Action
I believe this is just the beginning. These knowledge areas and the associated metrics are a work in progress, and I want to hear from you, my LinkedIn network of construction professionals.
What challenges do you face in managing construction projects?
What metrics or tools do you think would further enhance this methodology?
Your insights and feedback will help refine and enhance this system, making it even more robust and versatile. Together, we can advance construction project management to new heights of safety, quality, and sustainability.
Let’s collaborate to build a smarter future. Comment below or send me a message—I’m excited to hear your thoughts!
Top Categories
Popular Courses
Construction Engineering & Management
Construction Estimating & Bidding Process
CMBA: Business of Engineering- MBA Crash Course
Project Management Body of Knowledge
USGBC LEED Green Associate Study Group
Features of Our Site
Why CPMP.US?
CPMP.US is a website to collect information and link resources beneficial to emerging professionals interested in becoming a Construction Project Management Professional!
Intoducing Industry Leaders
Although we are based in Michigan, our community is comprised of Industry Leaders from all States
Newest Trends & Best Practices
Newest Trends and Latest Best Practices are introduced by all within the community
Open Source & Collaborative
All information on CQM Methodology is available for Free and open for collaboration
Testimonials
Trusted by Professionals and Students
5.0
Scorecard Rating
Client Satisfaction
Quality Project Management Program based on CQM Methodology is a "Robust” System!
Professional Quality Managers are "Elite Construction Project Managers", using the CQM Methodology will get you there!
Taking the Business of Engineering Course introduced me to all MBA Topics and how they apply to Construction Contractors!
Enthusiastic instructors, very insightful and beneficial Lectures. I'm enlightened with new ideas at every event!
Join CQM Community
Join the Construction Quality Management Community to learn about new Trends & Topics pertaining to becoming a CPMP
We need your help to make this website better! Don't hesitate to reach out to us if you have suggestions or you wish to contribute!








